Archives for April 2017
Quick Tip – Bezier Envelope and Fade Curves
A website for recording enthusiasts features an instructional video on how to change a sound track by simply clicking on it. The curve that signifies the way the music sounds is called a Bezier curve. The editor can do it by mouse or by clicking the keys Alt and Drag. In addition, the editor can use the mouse to adjust the process of fading sound tracks in or out. The program used to do this is called Reaper.
Read more: Quick Tip – Bezier Envelope and Fade Curves
SONAR 2017.03: MIDI, Back to the Future
A music blog offers a review of Sonar 2017.03, an update to a software program designed to manipulate musical instrument digital interface (MIDI) files. The updated program has an improved and easier to use control section. The stored music tracks are marked in colors for ease of tracking in music projects. The new program shows double the number of tracks as the previous version. The editor can easily edit tracks with a tool called Smart Swipe.
Read more: SONAR 2017.03: MIDI, Back to the Future
Bezier Envelope and Fade Curves Tips
In this quick tip video, we will be taught simple, intuitive and such a quick way of adjusting fades and envelopes.
The Default mouse-modifier of Alt/option-left-Drag on an envelope segment allows you to customize the curve shape called “Edit Envelope Segment Curvature”.
Watch video here: http://reaperblog.net/2017/03/bezier-curves/
How to Fix a "P-Pop" in Your Audio With A Sound Editor
 Here is how to fix a p-pop in a recording using sound editing software. If you do any voice recording at all, you’ve probably noticed this. No matter how hard you try, your “P” sounds (called “plosives”) will sometimes sound like small explosions in the audio.
These plosives sort of distort the audio recording for a second, sounding a bit like a low-frequency “splat.” Not pretty.
Here is how to fix a p-pop in a recording using sound editing software. If you do any voice recording at all, you’ve probably noticed this. No matter how hard you try, your “P” sounds (called “plosives”) will sometimes sound like small explosions in the audio.
These plosives sort of distort the audio recording for a second, sounding a bit like a low-frequency “splat.” Not pretty.
What causes it?
It’s what happens when a burst of wind hits a microphone. It’s especially pronounced when using a large diaphragm condenser mic like the one in the pic on the left – a Rode NT2-A. There are things you can do to minimize or prevent (shya!) them (like a pop filter), which is the best medicine. But when they do get recorded, you’ll want to know how to fix it after-the-fact. For this we use editing software. One of the wonderful things about audio editing in the computer age is that you get to use your eyes as well as your ears. I have edited so many p-pops (caused by what linguists call “plosives”) that I can recognize what they LOOK like on a computer screen even before I hear them. For my voice, the come out looking like a capital letter “N” in the waveform.How to fix it once it is recorded?
Since the plosive problem is basically caused by a rush of air from your lips hitting a microphone capsule fast and hard, what you have is a problem of volume. The plosive was too loud compared to everything around it. Not only that, but most of the too-loud bits are in the low end…the bass frequencies. So the fix would be to turn down the volume of your voice when it is hitting the “P.” In an audio editor, like Audacity (which is open source) you zoom in on the plosive and select everything right up until the voice actually becomes audible. In other words, if the word was “pot,” try not to get any of the -“ah” sound in your selection. You only want the “P” sound. Then you just use a volume reduction tool to turn down JUST the “P.” You may have to experiment (“undo” is the magic-bullet of computer audio editing!) with how much you turn it down, but that may be all you need to do.What if changing the volume doesn’t work?

Time needed: 5 minutes.
How to Fix a P-Pop in Your Audio
- Find the p-pop
Find where the p-pop happens in your recording by listening in headphones
- Highlight JUST the “p” Sound in Your Editing Software
Zoom in and highlight ONLY the “p” (or other plosive sound like “b,” etc.). Be careful not to select any of the vowel sound that comes after the “p” sound.
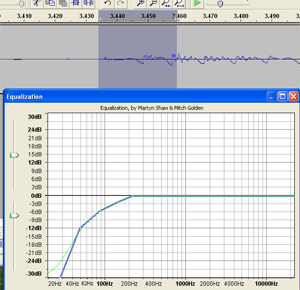
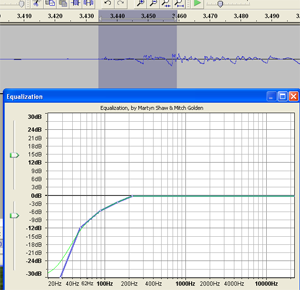
- Apply EQ Effect
Apply an equalizer effect (EQ) to the “p.” Reduce the low frequencies in a slope going down and to the left, starting with about 200 Hz.