 Mixing contest alert! PureMix is a site with audio recording, mixing and processing tutorial videos that make it sort of feel like you are working as a learning assistant to a professional studio engineer. Pretty cool stuff. You can check them out here: http://www.puremix.net/about-us.html.
Mixing contest alert! PureMix is a site with audio recording, mixing and processing tutorial videos that make it sort of feel like you are working as a learning assistant to a professional studio engineer. Pretty cool stuff. You can check them out here: http://www.puremix.net/about-us.html.
This month and next (April and May 2013), in association with Sweetwater Pro Audio and Dangerous Music (makers of high-end audio gear), are doing something very cool and fun. They are holding a massive mixing contest! How would something like that work? Well, they provide some audio files and you mix them together and render your version. In this case, they are providing tracks from singer, Liza Colby Sound’s song “Oh Baby.” Then you have until June 1st to create your own mix of the song using the files you downloaded. Sounds like a blast!
The rule is that you cannot change the arrangement. In other words, you cannot add other instruments or sounds. Your job will be to put use just panning, volume and effects to blend/mix everything together, then mix it down (see our article What Does It Mean to Mix Down Audio?) to one audio file and upload it to your SoundCloud account (it’s free) and then submit your masterpiece by June 1st, 2013.
Sweetwater, online retailers of recording and musical gear and one of the sponsors of this contest, will be announcing the winners of the contest during their annual GearFest event on June 21st and 22nd.
There will be 16 top candidates announced on June 21st, who will all be awarded prizes ranging from $3,990 (pair of Focal Twin6 Be speakers) for first prize, all the way down to a $269 value for a one-year subscription to PureMix. In between are various microphones and other audio goodness. You’ll get a list as soon as you sign up.
I already entered, downloaded my files and loaded them up in my DAW (“digital audio workstation” – another way of saying “multi-track recording software”) of choice – Reaper. Of course you can use whatever DAW you wish, or you could do it the old fashioned way and use analog tape if you have the gear for it.
What are you waiting for? Go sign up here: http://www.puremix.net/gearfestmixingcontest
Archives for April 2013
New Virtual Synthesizer From Sample Logic – Cyclone
 Sample Logic, makers of excellent virtual instruments and synthesizers such as The Elements Exp Virtual Instrument Library Software
Sample Logic, makers of excellent virtual instruments and synthesizers such as The Elements Exp Virtual Instrument Library Software and a lot more besides, has announced the release of their latest synth called Cyclone.
From the description on their website, it will use Native Instruments Kontakt (Cyclone will come with Kontakt player with 64-bit support) and be a combo instrument in that it plays sampled instruments (325 different types) as well as having the capability to act as a synthesizer, meaning you can alter the sounds with Sample Logic’s sequencer, arpeggiator and LFO (low-frequency oscillator), as well as the new Kontakt additive synthesis engine called “Wave.”
The kinds of instruments and sounds described, namely single instruments and multis giving you motion pads, cinematic instruments, dub-step type basses, electronic leads and much more. It sounded a lot to me like Omnisphere, by Spectrasonics. But Cyclone will be a bit a bit less expensive than Omnisphere’s $479, coming in at just under $300.
It’s scheduled to be released on April 22nd, 2013. So be ready if you’ve been looking for a great all-around virtual synth.
Elektron Octatrack Video – Using It As A Drum Machine
Here is a video from YouTube user, sbookholt, that shows how to load single-hit drum samples into the amazing Octatrack, by Elektron, which is a hardware sampler and sequencer. In the video, he shows you how he was able to dispense with the other Elektron product, Machinedrum, which is another programmable sequencer/synthesizer, but specializing in drums (you might have guessed that by the name of the product:)). Both products are pricey ($1,240 and $990, respectively), so it one can truly do the job of two in yhour particular rig/gig purposes, then you can save hundreds of dollars.
See the tutorial video below:
Obsessive In The Mixing Stage Of Recording
 There has been a lot of attention in the online audio recording space about mixing lately. It’s as if two things pervade the rest of the folks teaching and talking about home recording: the idea that music is the only thing people are doing (voice-over recording rarely involves much in the way of mixing – maybe background music and that’s usually it), and that if you are recording music, mixing is the most important part of doing it.
There has been a lot of attention in the online audio recording space about mixing lately. It’s as if two things pervade the rest of the folks teaching and talking about home recording: the idea that music is the only thing people are doing (voice-over recording rarely involves much in the way of mixing – maybe background music and that’s usually it), and that if you are recording music, mixing is the most important part of doing it.
Here are Home Brew Audio, we talk about both music AND voice-over recording. I know there is a very large proportion of the home recording space devoted to voice-over recording. Plus I am a voice-over actor. So we devote a significant percentage of our content to VO stuff.
The second seemingly pervasive presupposition is that between the mixing and record phases of a music recording project, it’s the mixing that is the most important. It follows, then, that a majority of producing time, assuming you do all your own recording (tracking), mixing and mastering (see our article on these three phases of a recording project – Recording Engineer, Mix Engineer and Mastering Engineer – Oh My), a majority of the time spent on the project should be mixing, as opposed to recording/tracking. I actually agree with that. It’s certainly true for me anyway.
My music niche – the renaissance re-enactors and medieval re-creation folks (mainly SCA) – has a LOT of musicians writing and recording songs. Most of them have the same basic equipment – a decent computer audio interface and a few decent mics along with some recording software. But (and this is going to sound a bit like boasting, but its true) so many people ask me what my secret is to getting such a professional sound compared to a majority of the other recordings out there in my niche. And you know what the answer is? OCD! OK, well that may be over-stating things a bit (no it isn’t!), but I spend a LOT more time mixing than recording. My recording to mix ratio is like 1:10.
I truly believe this is where the difference is made. Since I mix in a converted bedroom like most home recordists, I don’t have an ideal mixing space. So to get a good portable mix (one that will sound just as good in the car, on an iPod or on a large entertainment system), I have to literally mix for each of those playback systems. I start out with a draft mix, then take it with me in the car. It will have several balance problems – bass to loud or not loud enough, lead vocal uneven, can’t hear the drum, etc. So I take copious notes and go back to the computer and make adjustments. Then I take it with me in the car again. This repeats at least 3 or 4 times.
Then I will listen in headphones on an iPod. I’ll notice some problems that didn’t come across in the car, usually excess sibilance (SSS sounds) and maybe some more vocal mix issues. So I repeat the process until it now sounds good on both a car stereo and in the headphones with an iPod.
Finally, I’ll listen on the big stereo in the living room (CD player). I’ll notice some more problems there – typically to do with the way the lead vocal sits in the mix, but also problems in the high frequencies are usually revealed here, along with issues with reverb. So I go back and remix and repeat the same way as earlier until it sounds great on the big speakers. Then I listen to THAT mix in the car and on the iPod until it sounds great in all three places.
If I were wealthy and could afford to build an awesome acoustically ideal mixing/mastering listening space, along with a pair of high-end mixing loudspeakers (actually two or three different pair of monitors), I could save a lot of time in the mixing stage. But I can’t afford that yet. And until I do, I am going to get comfortable with my OCD in the mixing stage.
What Is Multiband Compression?
 Multiband compression is an incredible audio tool if you can get past the fact that it, like many other terms in audio, is a bit scary and technical sounding. It’s mainly used when mastering a song (see our article Mastering a Song – What Does It Mean? for a review of what mastering means), when everything is all mixed together and you only have one audio file. To understand what multiband compression is, you should first have a good idea what regular old compression is.
Multiband compression is an incredible audio tool if you can get past the fact that it, like many other terms in audio, is a bit scary and technical sounding. It’s mainly used when mastering a song (see our article Mastering a Song – What Does It Mean? for a review of what mastering means), when everything is all mixed together and you only have one audio file. To understand what multiband compression is, you should first have a good idea what regular old compression is.
In two previous articles, I wrote about compression basics – Improve Or Ruin Your Audio With an Effect Called Compression and Should You Use Compression In Audio Recording? So if you’re feeling a little rusty on your understanding, give those a quick read.
So back to our question – what is multiband compression? Assuming we know that compression means “turning down” audio loudness ONLY when it gets louder than a certain volume (i.e. the singer’s voice goes happily along with no volume reduction; but during that part in the chorus where he screams, it gets louder than the “threshold” you set on the compressor. So just during the screaming parts, the compressor turns the volume down), multiband compression does the same thing, but we get more control over which frequencies get compressed. Simple right?
Multiband Compression Versus EQ
OK, how about an example? If we have already mixed a song down (so it’s just one file now with all the instruments blended together), and it sounds fabulous except the bass sounds too loud for the song, we have two choices. We can try to use an equalizer effect to lower only certain frequencies (see our post What is Equalization, Usually Called EQ? for more on that). But equalizers turn down (or up) the volume at a targeted frequency or set of frequencies (or “band” or frequencies) regardless of how loud they are. Remember that a compressor won’t turn something down until it gets to a certain volume that you deem to be the place it should be turned down (called a “threshold”). So maybe the EQ isn’t controlling the bass, the low frequency parts of the song as much as you want. So now what?
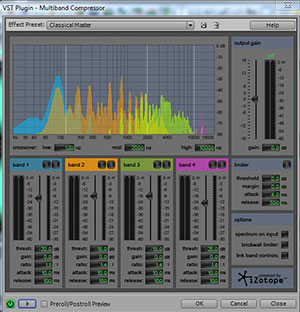
Well, if you have a multiband compressor (like the one pictured above, which is the iZotope multiband compression plugin that came with Adobe Audition 3), you can apply compression to JUST the low frequency, bass-y frequencies (most compressors operate across the entire frequency spectrum). Unlike an EQ, a compressor will allow everything to play with no volume reduction until it goes past the threshold volume level. So maybe your bass is all good except for one note that keeps popping out of the mix. Or maybe 80 percent of the song has a good bass mix, but during the pre-choruses, things start swimming in bass. A multiband compressor that is ONLY targeting bass frequencies will not do anything until those pre-choruses, which trigger the compression to start reducing bass. Then when the pre-chorus is over, and the bass drops back below the threshold, the compressor stops compressing; that is until the next time some bass notes get too loud, and then it kicks in again, etc. So in a way, a multiband compressor is sort of like EQ in that you can target certain frequency bands (more like a graphic EQ than a parametric EQ in that way). But since compression is different in that it only affects the audio above a specified loudness threshold, it may well be able to solve a problem that EQ cannot.
The multiband compressor plugin shown in the picture above allows you to set 4 different bands. You can just drag the lines on the graph that determine the border between two bands to select how you want to divide things up. Once you do that, you have all the normal compressor controls (threshold, ratio, etc.) available for each band, which you can now set individually and independently of the others. So you could apply a lot of compression in the bass range, say everything from 150 Hz down, while applying no compression at all to a mid-range band of 150 to 800 Hz, mildly compressing high mids of 800Hz to 2KHz, and not compressing anything above 2KHz – all simultaneously with one effect.
Mainly Used While Mastering
When a song is in the mixing stage, each instrument has its own track. So if the bass is too uneven, you can simply stick a compressor on the bass guitar track to even it out. And if the kick drum is interfering with the bass guitar, you can compress and/or EQ just the kick drum track. The same is true for every other frequency range. Maybe there is excess sibilance on the lead vocal. OK, just put an EQ on the lead vocal track and subtract loudness in the sibilance range, typically 4-8 KHz (for a review on sibilance and how to treat it, see our post How to Fix SSS-Sibilance in Your Audio With Sound Editing Software). If a guitar (or any instrument) is harsh and grating on your ears, you can put an EQ or compressor on the guitar track and treat that problem on that track. The point is that you can isolate the problem audio sources and treat them surgically on their own tracks.
 However, a mastering engineer receives “mixed down” audio (see our post What Does It Mean to Mix Down Audio?), all the instruments are already blended together into one file, so you cannot treat JUST the bass guitar, or JUST the lead vocal anymore. It’s like making a cake. Once everything is done and frosted, if you notice there was too much almond extract used in the recipe, well it’s too late to do anything about that. But a mastering engineer can come close to isolating elements of a mixed-down song (cake) using EQ and multiband compression, and may actually be able to reduce the almond extract flavor even after the cake is baked – to stretch that metaphor a little:).
However, a mastering engineer receives “mixed down” audio (see our post What Does It Mean to Mix Down Audio?), all the instruments are already blended together into one file, so you cannot treat JUST the bass guitar, or JUST the lead vocal anymore. It’s like making a cake. Once everything is done and frosted, if you notice there was too much almond extract used in the recipe, well it’s too late to do anything about that. But a mastering engineer can come close to isolating elements of a mixed-down song (cake) using EQ and multiband compression, and may actually be able to reduce the almond extract flavor even after the cake is baked – to stretch that metaphor a little:).
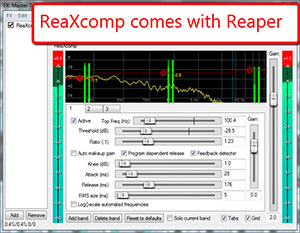
If you would like to try a multiband compressor, and you already have Reaper recording software, you’re in luck! One of the many effects plug-ins that come with Reaper is ReaXcomp, a multiband compressor. Most 3rd party MBC plug-ins cost at least $200 and go up from there. So the fact that you get one free with Reaper is pretty amazing. If you don’t already have Reaper, go download it now for free (http://www.cockos.com/reaper/download.php). They have a 60-day trial that is fully functional. And when the trial is done, you only pay $60 for the license. Then if you make $20,000 per year using their software, you pay for the commercial license for $250. And it’s all on the honor system! All versions of the software – trial, personal license, and commercial license – are identical and fully functional.
So now you know. Multiband compression is just a compressor that lets you apply different settings to different frequencies all at the same time. Go forth and create better music.
Cheers!
Ken